【本章纲要】
【本章内容】
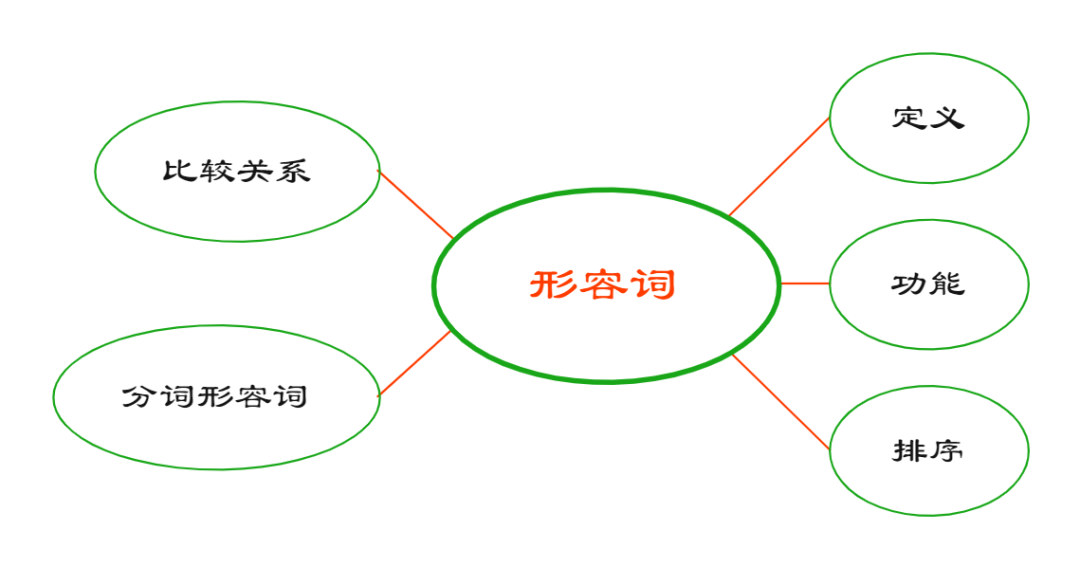
一、定义
形容词描述性的词,它们在上下文中用来描述名词。形容词通常回答诸如“哪个”、“什么种类”、“多少”等问题。
二、功能
1、作定语
如:
The old man asked a question.
That is a good book.
2、作同位语
一般成对使用,如:
The woman, beautiful and smart, knew what she was doing.
The winner, tired but happy, waved and smiled.
3、作表语
如:
The tickets are expensive.
She looked old.
三、排序
多个形容词同时修饰某个名词,其离所修饰的名词由远及近的先后顺序的排列规则如下:
a- 主观看法 (Lovely, beautiful, intelligent, nice, fine...)
b- 大小尺寸 (small, big, large, short, tall...)
c- 年龄新旧 (young, old...)
d- 形状外形 (round, slim, fat, square...)
e- 颜色 (white, green, red...)
f- 质地材料 (plastic, glass, wooden...)
g- 来源产地 (German, Russian, American...)
如:
a big square table
a lovely little town
an old plastic pipe
an expensive Scotch whiskey
a tall young woman
an Intelligent young Danish scientist
四、分词形容词
英语中有不少形容词是由动词的现在分词或过去分词转化而来的,如:
He is bored with his job.
He is boring.
五、比较关系
当要对两个人或物进行比较时,会有同级比较、比较级和最高级三种情况。同级比较一般采用“as...as...”的结构,比较级采用“more...than...”的结构,最高级采用“the most...in/of/among...”的结构。
形容词的比较级一般在词尾加-er,最高级一般在词尾加-est。
如:
She is as tall as Jane.
She runs faster than Jane.
She is the best student in her class.
【注意】
英语中有一些形容词是没有比较级和最高级的,它们被称为绝对形容词(Absolute adjectives),比如:dead, complete, basic。
 退休人员请注意!2024年1月起,养老金资格怎么认证,按这3种办法来一旦错过将暂停发放!退休人员请注意!2024年1月起,养老金资格怎么认证,按这3种办法来一旦错过将暂停发放!
退休人员请注意!2024年1月起,养老金资格怎么认证,按这3种办法来一旦错过将暂停发放!退休人员请注意!2024年1月起,养老金资格怎么认证,按这3种办法来一旦错过将暂停发放! 修改主页的方法( 修改被篡改的浏览器主页)修改主页的方法( 修改被篡改的浏览器主页)
修改主页的方法( 修改被篡改的浏览器主页)修改主页的方法( 修改被篡改的浏览器主页) 朋友的定义是什么(何谓“朋友”?)朋友的定义是什么(何谓“朋友”?)
朋友的定义是什么(何谓“朋友”?)朋友的定义是什么(何谓“朋友”?) 汽车清洗剂汽车专用(新手怎么选用汽车清洗剂?)汽车清洗剂汽车专用(新手怎么选用汽车清洗剂?)
汽车清洗剂汽车专用(新手怎么选用汽车清洗剂?)汽车清洗剂汽车专用(新手怎么选用汽车清洗剂?) 压声喊麦技巧和发声方法(喊麦怎么练声,需要掌握哪些技巧)压声喊麦技巧和发声方法(喊麦怎么练声,需要掌握哪些技巧)
压声喊麦技巧和发声方法(喊麦怎么练声,需要掌握哪些技巧)压声喊麦技巧和发声方法(喊麦怎么练声,需要掌握哪些技巧) 开卷是否有益是什么意思(开卷有益吗?)开卷是否有益是什么意思(开卷有益吗?)
开卷是否有益是什么意思(开卷有益吗?)开卷是否有益是什么意思(开卷有益吗?)